Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
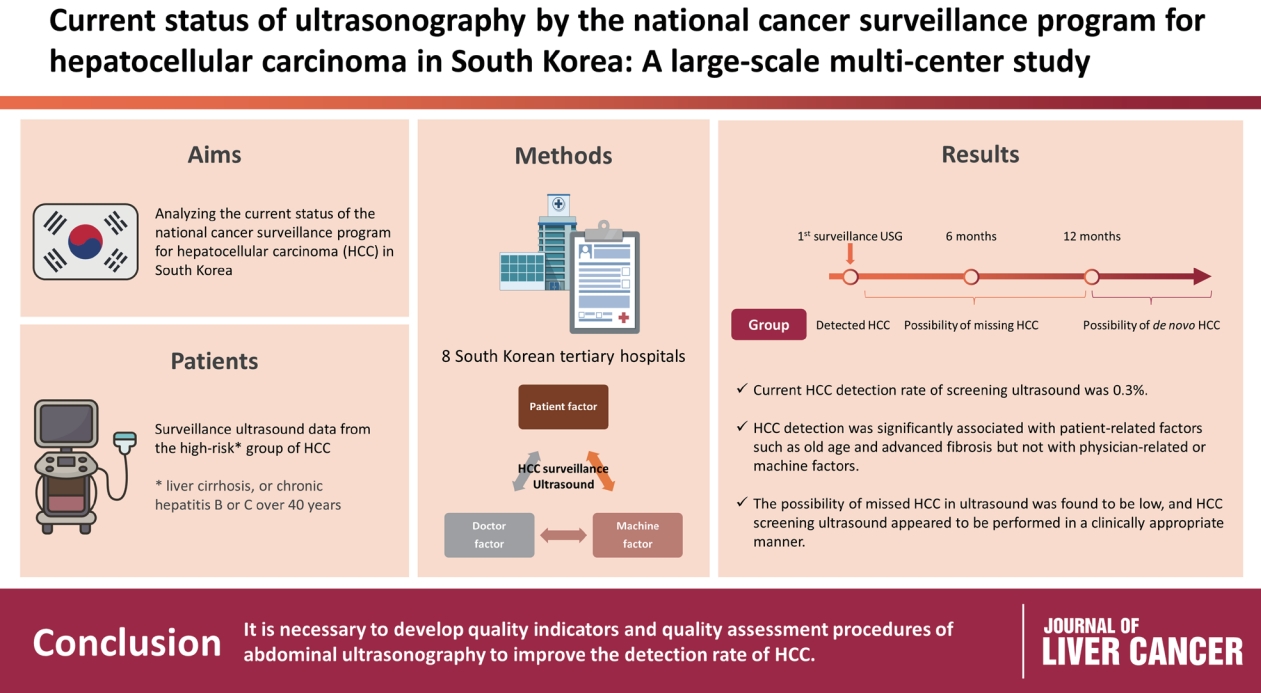
- Current status of ultrasonography in national cancer surveillance program for hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea: a large-scale multicenter study
- Sun Hong Yoo, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Gyune Kim, Jung Hyun Kwon, Han-Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim, Do Seon Song, Seong Hee Kang, Moon Young Kim, Young-Hwan Ahn, Jieun Han, Young Seok Kim, Young Chang, Soung Won Jeong, Jae Young Jang, Jeong-Ju Yoo
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):189-201. Published online March 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.03.11
- 1,599 Views
- 65 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
Abdominal ultrasonography (USG) is recommended as a surveillance test for high-risk groups for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to analyze the current status of the national cancer surveillance program for HCC in South Korea and investigate the effects of patient-, physician-, and machine-related factors on HCC detection sensitivity.
Methods
This multicenter retrospective cohort study collected surveillance USG data from the high-risk group for HCC (liver cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B or C >40 years of age) at eight South Korean tertiary hospitals in 2017.
Results
In 2017, 45 experienced hepatologists or radiologists performed 8,512 USG examinations. The physicians had a mean 15.0±8.3 years of experience; more hepatologists (61.4%) than radiologists (38.6%) participated. Each USG scan took a mean 12.2±3.4 minutes. The HCC detection rate by surveillance USG was 0.3% (n=23). Over 27 months of follow-up, an additional 135 patients (0.7%) developed new HCC. The patients were classified into three groups based on timing of HCC diagnosis since the 1st surveillance USG, and no significant intergroup difference in HCC characteristics was noted. HCC detection was significantly associated with patient-related factors, such as old age and advanced fibrosis, but not with physician- or machine-related factors.
Conclusions
This is the first study of the current status of USG as a surveillance method for HCC at tertiary hospitals in South Korea. It is necessary to develop quality indicators and quality assessment procedures for USG to improve the detection rate of HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term HBsAg Titer Kinetics with Entecavir/Tenofovir: Implications for Predicting Functional Cure and Low Levels
Soon Kyu Lee, Soon Woo Nam, Jeong Won Jang, Jung Hyun Kwon
Diagnostics.2024; 14(5): 495. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

Case Reports
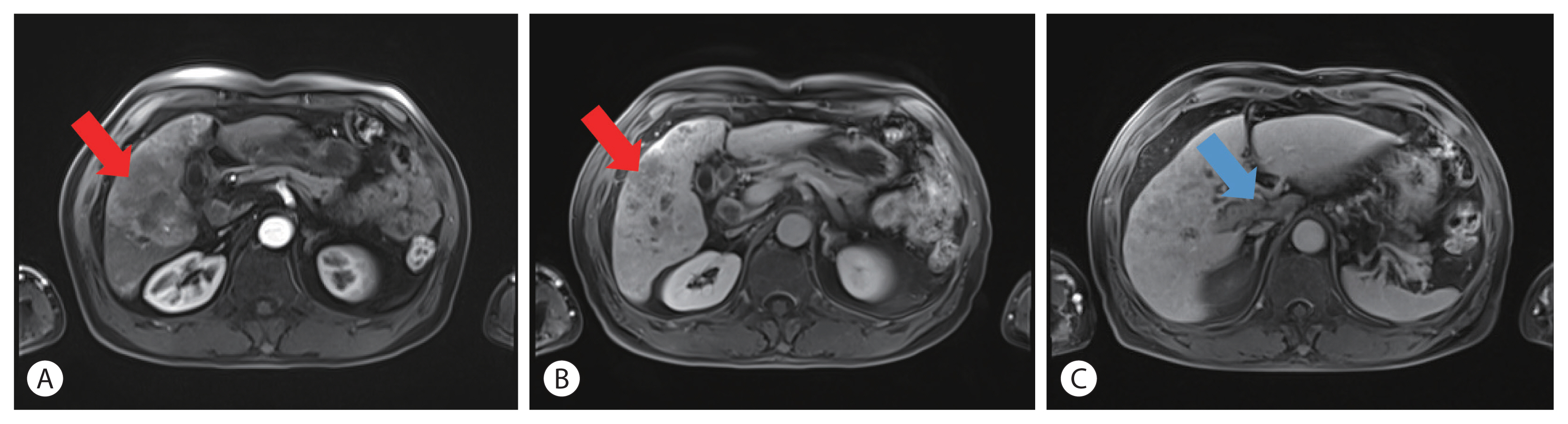
- A case report of a patient presented with skin ulcer after treatment of lenvatinib
- Serin Cha, Dong Woo Kim, Jung Wan Choe, Tae Hyung Kim, Seung Young Kim, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):194-198. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.20
- 3,298 Views
- 78 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 60-year-old man diagnosed with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presented to the hospital with pain in the perineal region. He had been taking lenvatinib every day for 2 months after he was diagnosed with HCC with metastases to the lymph node, small bowel mesentery, and retroperitoneal space. Enhanced abdominal computed tomography revealed mild elevation in intensity in the perineal subcutaneous tissue with subcutaneous emphysema. The patient was diagnosed with Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events grade 3, skin ulceration of stage IV with full-thickness skin loss and tissue necrosis in the muscular layer. The patient was taken off the medication with prescription of antibiotics, and after 3 weeks, the skin has fully recovered. This is the first report of an HCC patient who presented with a skin ulceration of stage IV after lenvatinib treatment. We recommend stopping the medication immediately and changing to alternative treatments with appropriate supportive care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multiple lenvatinib‐associated skin ulcers: A case report and literature review
Soo Hyun Jeon, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Sung Eun Chang, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung
Australasian Journal of Dermatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multiple lenvatinib‐associated skin ulcers: A case report and literature review

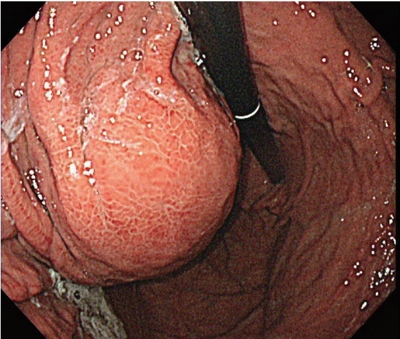
- Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Dae-ha Kim, Minkoo Kim, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):154-158. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
- 3,449 Views
- 47 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.

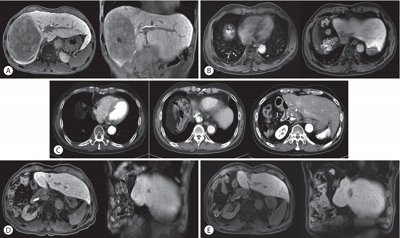
- Long-term Disease-free Survival after Trimodality Treatment of Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and Right Atrium
- Sunmin Park, Won Sup Yoon, Hyung Joon Yim, Chai Hong Rim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):149-153. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.149
- 3,571 Views
- 73 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) involving the inferior vena cava (IVC) and/or right atrium (RA) is a rare and intractable disease. A standard treatment has not been established yet, owing to the rarity of disease and difficulties in the therapeutic treatment. Herein, we report the case of a patient who had recurrent HCC (after a prior lobectomy) involving both IVC and RA and underwent multimodality treatments including external beam radiotherapy and transarterial chemotherapy, followed by sorafenib treatment. The disease was well controlled with local treatments and sustained for 7 years until last follow-up after the systemic treatments. Our case shows a possibility of long-term survival for patients affected by HCC involving IVC and/or RA, after a rigorous multimodality treatment strategy.

Original Articles
- An Analysis for Survival Predictors for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Failed to Sorafenib Treatment in Pre-regorafenib Era
- Chan Uk Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Minjin Lee, Sehwa Kim, Young Kul Jung, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):117-127. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.117

- 4,224 Views
- 64 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Sorafenib is the standard treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We aimed to investigate the prognosis predictors and the role of second-line cytotoxic systemic chemotherapy (CSC) in patients with advanced HCC after sorafenib discontinuation in the pre-regorafenib era.
Methods
From 2007 to 2015 in the pre-regorafenib era, the medical records of 166 HCC patients, who had permanently discontinued sorafenib, were retrospectively reviewed. For further analysis of survival factors after sorafenib treatment failure, we compared the survival of patients who had maintained liver function after second-line treatment with the best supportive care (BSC) group and selective BSC (SBSC) group.
Results
After discontinuation of sorafenib, median overall survival (OS) was 2.8 (1.9-3.7) months. The OS in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to adverse effect, progression, and poor clinical condition were 5.5 (2.4-8.6), 5.5 (2.2-8.9), and 0.9 (0.5-1.3) months, respectively (P<0.001). The independent predictive factors of survival after sorafenib failure were serum level of bilirubin and albumin, α-fetoprotein, discontinuation cause, and second-line CSC. In comparison with survival between second-line CSC and BSC group, the CSC group showed better survival outcome compared to the BSC group (10.6 vs. 1.6 months, P<0.001) and SBSC group (10.6 vs. 4.2 months, P=0.023).
Conclusions
The survival after sorafenib failure in patients who discontinued sorafenib due to progression and adverse effects was significantly better than in those who discontinued treatment due to clinical deterioration. In the pre-regorafenib era, patients who received second-line CSC showed better survival than those who received only supportive care after sorafenib failure.

- Factors Affecting Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: Implications for Future Therapeutic Strategies
- Sang Jun Suh, Hyung Joon Yim, Dong Won Lee, Jong Jin Hyun, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Soon Ho Um
- J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):60-71. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.60
- 2,126 Views
- 23 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) exhibits poor prognosis. The aim of this study is to evaluate factors associated with survival of HCC patients with PVTT to suggest better therapeutic options.
Methods
Patients with HCC which were newly diagnosed at three tertiary hospitals between January 2004 and December 2012, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, Barcelona Clinic of Liver Cancer stage C patients with PVTT were identified. Factors affecting overall survival (OS) were analyzed and efficacies of the treatment modalities were compared.
Results
Four hundred sixty five patients with HCC and PVTT were included. Liver function, tumor burden, presence of extrahepatic tumor, alfa fetoprotein, and treatment modalities were significant factors associated with OS. Treatment outcomes were different according to the initial modalities. OS of the patients who received hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), sorafenib, systemic cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation therapy (without combination), and supportive care were 27.8, 7.1, 6.7, 5.3, 2.5, 3.0, 1.8, and 0.9 months, respectively (P<0.001). Curative-intent treatments such as hepatic resection or RFA were superior to noncurativeintent treatments (P<0.001). TACE or HAIC was superior to sorafenib or systemic chemotherapy (P<0.001). Combining radiotherapy to TACE or HAIC did not provide additional benefit on OS (P=0.096).
Conclusions
Treatment modalities as well as baseline factors significantly influenced on OS of HCC patients with PVTT. Whenever possible, curative intent treatments should be preferentially considered. If unable, locoregional therapy would be a better choice than systemic therapy in HCC patients with PVTT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies
Keera Kang, Sung Kyu Song, Chul-Woon Chung, Yongkeun Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2020; 24(3): 243. CrossRef
- Value of surgical resection compared to transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis of hazard ratios from five observational studies

Case Reports
- A Case of Successful Hepatic Resection after Insufficient Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiation Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Invasion
- Seong Kyun Na, Hyung Joon Yim, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):118-122. Published online September 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.118
- 927 Views
- 5 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein invasion has a poor prognosis. Treatments such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), radiation therapy (RT), sorafenib are done as a first line treatment. But in case of incomplete response to first line treatment, there’s no established guideline about salvage treatment. We present a 47 year-old male who was diagnosed as HCC with portal vein invasion. He was treated with RT and repeated TACE, but remnant viable tumor was observed. Surgical resection was performed as a salvage treatment, and HCC was completely removed. He has been followed up over 3 years, but there was no recurrence.

- Regression of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Lung Metastasis in Response to Sorafenib
- Dae-ha Kim, Gee ho Min, Dong-won Lee, Ke Ryun Ahn, Ji Hye Kim, Snag-Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):57-62. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.57
- 1,053 Views
- 6 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sorafenib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits Raf kinase and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor intracellular kinase pathway and is the first agent to demonstrate a statistically significant improvement in overall survival for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, there were few cases of partial or complete response reported in the previous studies. We herein report a case of dramatic partial response in a patient who had advanced HCC with multiple lung metastasis and portal vein thrombosis treated with sorafenib.

- A Case Report of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Stereotactic Radiation Therapy before Liver Transplantation in a Decompensated Cirrhosis with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sang Hoon Kim, Joo Hee Park, Sang Jun Suh, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
- J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):135-138. Published online September 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.135
- 944 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liver transplantation is the only curable treatment modality for hepatocellular carcinoma with advanced liver cirrhosis. While treatment outcome of the liver transplantation is improving, time needed to standby until the surgery is getting longer because of both the lack of liver donors and increasing demands for the transplantation. Therefore, importance of bridging therapy before the liver transplantation is recently highlighted. We herein report our recent experience about a patient who successfully undergone transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and stereotactic radiation therapy (START) as bridging therapy and later had liver transplantation operation. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:135-138)

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Tumor Thrombus in Inferior Vena Cava and Right Atrium
- Hyun Jung Lee, Hyung Joon Yim, Hwan Hoon Chung, Seung Hwa Lee, Hae Rim Kim, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Sang Woo Lee, Jai Hyun Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):141-145. Published online September 30, 2012
- 606 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), tumor thrombus in inferior vena cava (IVC) and right atrium (RA) are not uncommon findings and are usually associated with extremely poor outcome. Although aggressive surgical interventions such as extracorporeal circulation and tumor excision have been performed, the reported results were still unsatisfactory. Herein, we report the favorable result of combined treatment with radiation therapy and transarterial chemoembolization in a patient with advanced HCC with extensive tumor thrombus through the IVC into the RA. In conclusion, noninvasive combined modalities, such as transarterial chemoembolization and radiation therapy may sometimes provide effective palliation for patients with far advanced HCC with IVC/RA tumor thrombus and who are not candidates for alternative treatment options.

- Two Cases of Small (< 1 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jin Yong Jung, Sun Young Yim, Chang Ha Kim, Jin Dong Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Ho Sang Ryu, Min Ju Kim, Beom Jin Park, Soon Ho Um
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):37-41. Published online February 28, 2012
- 514 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tumor size is one of the most important factors for decision of therapeutic plan and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). If the diagnosis of HCC is made earlier in its small size, the prognosis is better. However the diagnosis of small HCC is not easy because small HCC lacks the typical clinical and radiologic feature. We experienced two cases of small HCC less than 1 cm that was confirmed after first treatment.

- A Case of Successful Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with a Pulmonary Metastasis by Combining Pulmonary Wedge Resection and Sorafenib
- Sun Jae Lee, Hyung Joon Yim, Hwan Hoon Chung, Hae Rim Kim, Eileen L. Yoon, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Rok Son Choung, Sang Woo Lee, Jai Hyun Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):67-70. Published online February 28, 2012
- 584 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - 35-year-old female patient was diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma and underwent hepatic resection. 12 months after hepatic resection, serum AFP rose (119.6 ng/mL) but no definite recurrence was found on imaging modalities. 30 months after hepatic resection, serum AFP rose up to 1008.5 ng/mL and metastatic nodule was found in right lower lung in chest CT. Video assisted thoracoscopic wedge resection was performed and 400 mg/day of sorafenib was intiated. Serum AFP returned to normal range after 2 months of pulmonary resection. No evidence of recurrence is noted after 30 months of pulmonary resection. We think that pulmonary resection plus sorafenib combination therapy resulted in favorable treatment outcome in this patient.

- A Case of Aggressive Treatment with Transarterial Embolization Using Drug-Eluting Beads for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis Patient
- Eileen L. Yoon, Hyung Joon Yim, Hwan Hoon Chung, Seung Hwa Lee, Hae Rim Kim, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Sang Woo Lee, Jai Hyun Choi
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):190-194. Published online September 30, 2011
- 542 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Conventional transarterical chemoembolization (TACE) is the first-line treatment for patients with intermediate stage of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, irreversible liver failure after the procedure is one of the most feared complications and therefore, decompensated Child-Pugh C patients may not be the indication of the conventional TACE. Drug-eluting beads loaded with doxorubicin is a novel drug delivery embolization system and reported to have non inferior efficacy compared to conventional TACE. Also drug-eluting beads loaded with doxorubicin is associated with lower rates of acute liver failure after the procedure and lower rates of systemic toxicity of the chemotherapeutic agents. Herein, we report a case of aggressive treatment with transarterial embolization using drug-eluting beads loaded with doxorubicin for HCC in decompensated liver cirrhosis patient who was not eligible for conventional TACE treatment.

Review Article
- New Treatment Response Evaluation Criteria and Current Therapeutics for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hyung Joon Yim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):17-23. Published online June 30, 2009
- 506 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There has been no proven effective therapy in the setting of advanced HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma) according to BCLC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer). Targeted therapy opened a new era in this subset of patients. Although sorafenib showed survival benefit, objective tumor response is uncommon, while systemic chemotherapies sometimes show partial tumor response without statistically significant survival benefits. These findings suggest evaluation of treatment response should not depend on conventional treatment response evaluation criteria. Overall survival is now considered to be the most important endpoint and time to disease progression can be secondary endpoint. Time to recurrence is the primary endpoint after the curative therapy. Currently, targeted therapy in addition to known curative or palliative therapy is now under investigation for synergistic effects, and new therapeutic agents are under development. Such advancement in the treatment of HCC will certainly have a great impact on patients’ survival in the near future.

Case Report
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Early Multiple Recurrences after Liver Resection
- Jae Hong Ahn, Hyung Joon Yim, Seung Young Kim, Jeong Han Kim, Yeon Seok Seo, Seung Hwa Lee, Hwan Hoon Chung, Tae Jin Song, Hong Sik Lee, Sang Woo Lee, Soon Ho Um, Jai Hyun Choi, Ho Sang Ryu
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2009;9(1):29-32. Published online June 30, 2009
- 525 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic resection is a standard curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) although only 10~30% of patients are indicated due to advanced stage or poor hepatic reserve. Five year survival rate after resection was reported as a mean of 55% (25~93%), but cases of early recurrence after hepatic resection had poor prognosis. As early recurrence after hepatic resection is the one of the most important factors that determines the prognosis, many investigators have been trying to determine the factors associated with early recurrence. We report a case of early multiple recurrence of HCC after curative hepatic resection probably due to microvascular invasion of tumor and too close resection margin. We would like to suggest that additional prophylactic measures need to be sought in this group of patients because these factors may influence on early recurrence.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter